f:ajax è un tag JSF che aggiunge il meccanismo delle request asincrone a molti componenti UI.
pagina con supporto ajax:
ProvaAjax.xhmtl
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN”
“http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd”>
<html xmlns=”http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml”
xmlns:f=”http://java.sun.com/jsf/core”
xmlns:h=”http://java.sun.com/jsf/html”>
<h:body>
<h3>JSF 2.0 + Ajax Hello World Example</h3>
<h:form>
<h:inputText id=”name” value=”#{provaTag.name}” ></h:inputText>
<h:commandButton value=”Try Me” >
<f:ajax execute=”name” render=”output” listener=”#{provaTag.handleEvent}” />
</h:commandButton>
<h2><h:outputText id=”output” value=”#{provaTag.message}” /></h2>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
nel tag f:ajax:
– execute=”name”, indica che il componente con id “name” deve essere mandato al server.
– render=”output”, indica che il componente con id “output” dovrà, dopo la request ajax, essere aggiornato.
– listener=“#{provaTag.handleEvent}”, indica il metodo del bean da chiamare.
ProvaTag.java
import javax.faces.bean.ManagedBean;
import javax.faces.bean.SessionScoped;
import javax.faces.event.AjaxBehaviorEvent;
import java.io.Serializable;
@ManagedBean
@SessionScoped
public class ProvaTag implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String name;
private String message;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getMessage(){
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public void handleEvent(AjaxBehaviorEvent event) {
message = “Hello World:”+ name;
}
}
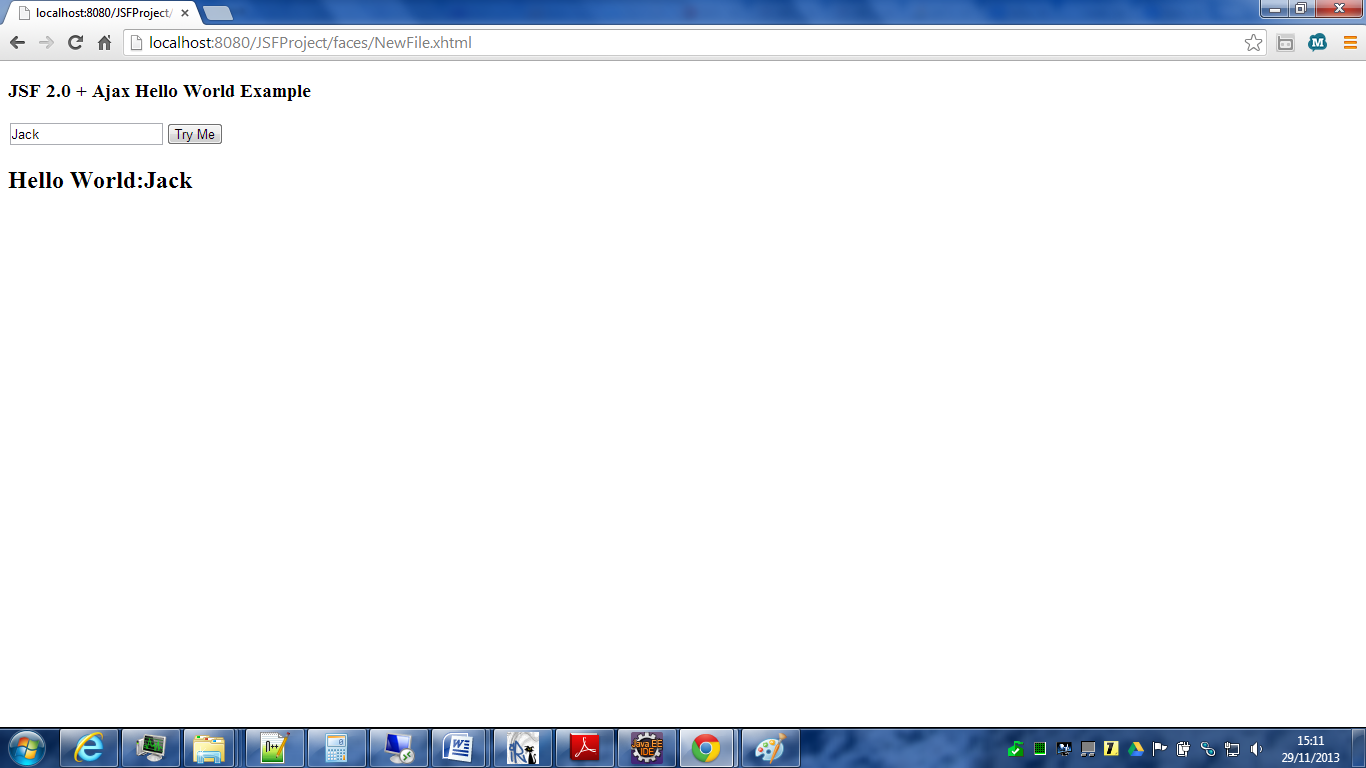
risultato: